Document Type : CASE STUDY
Authors
- A. D. Santoso
- T. Handayani
- D. Pinardi
- K. Kusrestuwardani
- N. Widyastuti
- I. N. Djarot
- J. Haryanti
- A. I. Sitomurni
- H. Apriyanto
Research Centre for Sustainable Production System and Life Cycle Assessment, National Research and Innovation Agency, Indonesia
Abstract
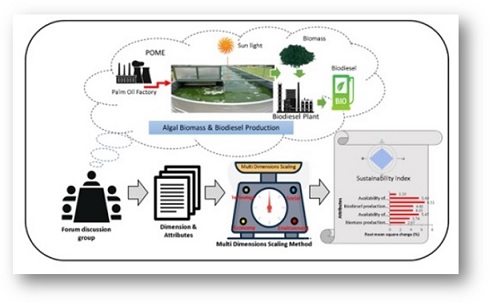
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Palm oil mill effluent is a liquid waste produced at a palm oil mill industry during the production process containing abundant organic pollutants such as nitrogen and phosphorus that will be harmful to the environment. However, palm oil mill effluent as a nutrient for the growth of microalgae has the potential for pollutant removal as well as algae biorefinery products such as biofuel, functional food and many others. This research objectives to analyze the sustainability of the microalgae biomass production for bio-refinery based on the sustainability index assessment.
METHODS: The primary data was compilated via the questionnaires to researchers in the community of microalgae as well as scientific judgment by experts as respondents. Data is processed and analyzed using the multidimensional scaling Rapfish program. Data analyzed was conducted by analyzing four dimensions: social, economic, ecological, and technological dimensions which consisting of 47 attributes.
FINDINGS: The result showed that the sustainability index calculated was 73.53 percent (good), which indicates the process has the potential to be developed while paying attention to leverage factors in every dimension of the sector. Analysis of each dimension on the 4 dimensions shows that the environment dimension is lowest in 67.30 percent, while the economy, technology and social dimension are 70.99 percent, 73.67 percent and 82.17 percent, respectively. Some leverage attributes that require more attention in order to improve sustainability are management experience and skills (in environment dimension), involvement of family member (in the social dimension), the productivity level (in economic dimension), and management of experience and skill (technological dimention).
CONCLUSION: Based on the prospective analysis, it is known that there are 4 key factors or dominant factors that are very influential in the microalgae supply system, namely production, productivity, land conversion, consumption per capita and population. It is still necessary to do further research for the utilization of microalgae biomass into value-added products with an optimal, technically, economically, environmentally and socially sustainable system. The study provides insights on the feasibility of the proposed sustainable concept in Indonesia for the government to arrange policies and programs.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
- Microalgae production from POME wastewater has a good sustainability index (73.53%) indicating this process has potential for development while considering factors influencing sustainability;
- There is a need for further research on microalgae biomass to increase the yields of value-added products using optimal, sustainable, and economical cultivation systems;
- The calculation of a sustainability index for the production of biomass and biodiesel using microalgae provides important information on sustainability;
- Implementation of the sustainable microalgae production concept proposed in the present study appears to have high feasibility in Indonesia.
Keywords
Main Subjects
OPEN ACCESS
©2023 The author(s). This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit:
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
PUBLISHER NOTE
GJESM Publisher remains neutral concerning jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
CITATION METRICS & CAPTURES
Google Scholar | Scopus | Web of Science | PlumX Metrics | Altmetrics | Mendeley |
CURRENT PUBLISHER
GJESM Publisher


Letters to Editor
[1] Letters that include statements of statistics, facts, research, or theories should include appropriate references, although more than three are discouraged.
[2] Letters that are personal attacks on an author rather than thoughtful criticism of the author’s ideas will not be considered for publication.
[3] Letters can be no more than 300 words in length.
[4] Letter writers should include a statement at the beginning of the letter stating that it is being submitted either for publication or not.
[5] Anonymous letters will not be considered.
[6] Letter writers must include their city and state of residence or work.
[7] Letters will be edited for clarity and length.
Send comment about this article