Document Type : CASE STUDY
Authors
1 Department of Social Studies, Faculty of Regional Development and International Studies, Mendel University in Brno, Brno, Czech Republic
2 Department of Corporate Economy, Faculty of Economics and Administration Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic
Abstract
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: This paper focuses on the development of Czech laws of water resource protection. The presented research examines the statistical data of the number and type of legislative acts concerning to water protection issued in the Czech Republic during the period 1990-2019. Several types of legislative acts are followed in administrative law and statistically compared by the development in time and its type. The survey focuses on general water protection acts, water sewage management, agriculture sector, hygiene standards, and the protection of the basins of Czech rivers (e.g., blue water and gray water).
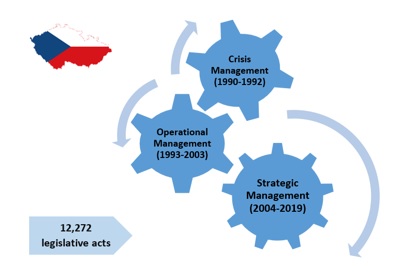
METHODS: The analysis firstly concerns to the development of the number of legislative acts during 1990-2019 and secondly discusses a diversification of the legislative acts types (laws, decrees, resolutions, regulations, and strategic plans). A total of 12,272 legislative acts is analyzed during three phases of Czech modern history: 1990-1992 (Czechoslovakia), 1993-2003 (Czech Republic before its accession to the European Union), and 2004-2019 (Czech Republic in the European Union).
FINDINGS: Statistical elaboration of legislative acts proves that it is possible to determine different types of water management over time. Protection of water resource management in the Czech Republic was forming from crisis management (1990-1992), via operational management (1993-2003) to strategic management (2004-2019). Current trends after 2020 show a new trend towards integral management.
CONCLUSION: Findings provide better understanding of changeable importance of water protection and management attitudes in the Czech Republic in reaction to the development of society.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
- The development of water protection in the Czech Republic in the period 1990-2019 has not taken place stable continuously, but in three qualitatively different stages of adopting legislative norms;
- The legislative aspects of Czech social development (crisis, operational, strategic or integral) influenced the approach to water protection, it is not possible to determine a single type of water management in period 1990-2019;
- The Czech Republic, as the so-called "Roof of Europe", where no river flows in, for the future must implement Integral water management.
Keywords
- Crisis management
- Czech Republic
- Integral management
- Legislative Act
- Operational management
- Strategic management
- Water management
Main Subjects
OPEN ACCESS
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Citation Metrics & Captures
Google Scholar | Scopus | Web of Science | PlumX Metrics | Altmetrics | Mendeley |


Letters to Editor
[1] Letters that include statements of statistics, facts, research, or theories should include appropriate references, although more than three are discouraged.
[2] Letters that are personal attacks on an author rather than thoughtful criticism of the author’s ideas will not be considered for publication.
[3] Letters can be no more than 300 words in length.
[4] Letter writers should include a statement at the beginning of the letter stating that it is being submitted either for publication or not.
[5] Anonymous letters will not be considered.
[6] Letter writers must include their city and state of residence or work.
[7] Letters will be edited for clarity and length.
Send comment about this article