Document Type : ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE
Authors
- V. G. Shcherbak 1
- I. Gryshchenko 1
- L. Ganushchak-Yefimenko 1
- O. Nifatova 1
- V. Tkachuk 2
- T. Kostiuk 2
- V. Hotra 3
1 Department of Entrepreneurship and Business, Kyiv National University of Technologies and Design, Kyiv, Ukraine
2 National University of Life and Environmental Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
3 Department of Economic Sciences, Uzhgorod National University, Uzhgorod, Ukraine
Abstract
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: A new wave of Covid-19 pandemic has worsened the epidemiological situation in Ukraine. This caused the need to tighten quarantine measures that have been introduced since 31.08.2020. The conducted analysis showed that there are 3 groups of technologies for digital contact tracing: from maximum (25%) to minimum (20%). Objective of the study is to develop an exchange platform to track the spread of COVID-19 in rural areas.
METHODS: Factor analysis identified key factors of COVID-19 virus spread. Cluster analysis identified clusters of COVID-19 spread. Taxonomy method established the limits of using contact tracing methods. Discriminatory method makes it possible to change the applied contact tracing method.
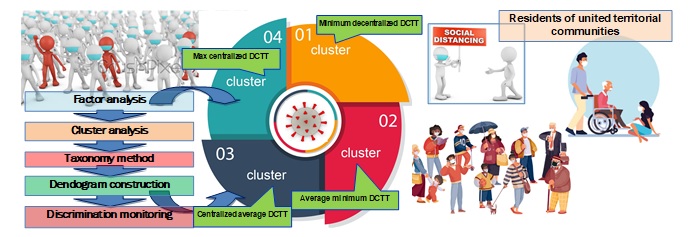
FINDINGS: The results showed that the identified factors (medico-demographic special features of Covid-19 virus spread; rural infrastructure to counteract the infection) describe in total 83.24% of the data processed. Specified 4 clusters differ in the level of susceptibility of the population to COVID-19 and infrastructure development: from minimum (33% of the united territorial communities) to maximum - 13% of the united territorial communities. The value of the integral indicator calculated provides means for establishing the maximum (8.5) and the minimum (2) limit of changes in the method of digital contact tracing.
CONCLUSION: The developed methodology was implemented on the basis of the united territorial communities of Sumy region. Monitoring of changes in the epidemiological situation made it possible to justify the need to change the contact tracing model, which will reduce the epidemiological level in the region as a whole by 30%.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
- Two key factors of COVID-19 spread and resistance in rural areas were identified. The first factor (medico-demographic features of COVID-19 virus spread) reasons 51.25% of the processed data. The second factor (rural infrastructure aimed at combatting the infection) reasons 31.99% of the processed data;
- 4 clusters were identified, which differ in the level of infection and resistance of COVID-19 in rural areas of Sumy region;
- Different DCTT models are suggested to identify clusters according to the susceptibility level of population to COVID-19 and infrastructure development: from minimum (33% UTC of the first cluster) to maximum (centralized) - 13% UTC of the fourth cluster;
- The developed methodology makes it possible to diagnose the prevalence rates of COVID-19, to monitor changes in the epidemiological situation in the united territorial communities, to suggest appropriate models for tracking contacts, which will reduce the epidemiological level by 30% in general.
Keywords
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Digital contact tracing technologies (DCTТ model)
- Indicators
- Monitoring
- Rural areas
- United territorial communities (UTC)
Main Subjects
OPEN ACCESS
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Citation Metrics & Captures
Google Scholar | Scopus | Web of Science | PlumX Metrics | Altmetrics | Mendeley |


Letters to Editor
[1] Letters that include statements of statistics, facts, research, or theories should include appropriate references, although more than three are discouraged.
[2] Letters that are personal attacks on an author rather than thoughtful criticism of the author’s ideas will not be considered for publication.
[3] Letters can be no more than 300 words in length.
[4] Letter writers should include a statement at the beginning of the letter stating that it is being submitted either for publication or not.
[5] Anonymous letters will not be considered.
[6] Letter writers must include their city and state of residence or work.
[7] Letters will be edited for clarity and length.
Send comment about this article