Document Type : ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE
Authors
1 Department of Agricultural Microbiology, Agricultural and Biological Research Division, National Research Center, Egypt
2 Department of Agricultural Microbiology, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Egypt
Abstract
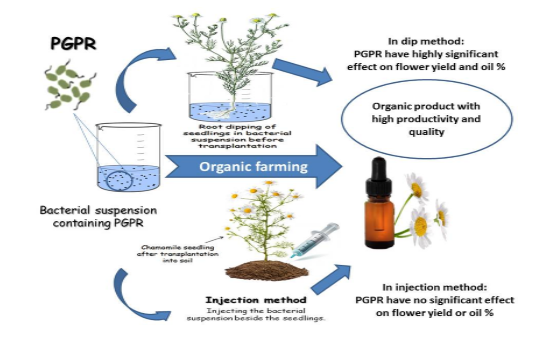
Chamomile is one of the most wide spread medicinal plant cultivated in Egypt. This work aimed at enhancement of blossoms and oil production of chamomile plants via biofertilization with PGPRs under organic farming system. In this study, 6 bacterial strains were applied using two different inoculation techniques. The first application method was throughout soaking the roots of seedlings in the bacterial suspension before transplanting. The second technique was by adding the bacterial inocula to soil 2 weeks after transplantation. The results showed that root dipping method displayed high impact on the yield of chamomile blossoms and essential oil percentage. Furthermore, the soil application of the bacterial inocula didn’t show any significant impact in this respect. Where Paenibacillus polymyxa, Bacillus subtilis, Serratia plymuthica and Streptomyces subrutilus increased the dry weight of chamomile blossoms compared to the control, essential oil content increased significantly in case of Serratia plymuthica, Stenotrophomonas rhizophyla and Bacillus subtilis. The current results also indicated that bacterial strains produced the highest indole-3-acetic acid and gibberellic acid resulted in the highest yield of both flowers and essential oil.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
- Improvement of chamomile plant production through biofertilization under organic farming system was evaluated;
- Chamomile blossom and oil yield enhanced by submerging the seedlings root in the Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria suspension;
- Bacterial strains producing phytohormones showed the positive impact on blossoms and oil yield.
Keywords
Main Subjects


Letters to Editor
[1] Letters that include statements of statistics, facts, research, or theories should include appropriate references, although more than three are discouraged.
[2] Letters that are personal attacks on an author rather than thoughtful criticism of the author’s ideas will not be considered for publication.
[3] Letters can be no more than 300 words in length.
[4] Letter writers should include a statement at the beginning of the letter stating that it is being submitted either for publication or not.
[5] Anonymous letters will not be considered.
[6] Letter writers must include their city and state of residence or work.
[7] Letters will be edited for clarity and length.
Send comment about this article